Domain Name System (DNS) is an industry standard TCP/IP (Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) suite protocol. Basically, DNS is a “user name resolution” system; it converts alpha-numeric names into numeric IP address and vice-versa.
Understanding DNS
When you type in Google.com in your browser’s address bar, it’s a DNS server that maps this website name (i.e. Google.com) to the IP address of the server where the website is actually hosted.
How Does DNS Work
DNS protocol works as a “Server DNS” and “Client DNS.”
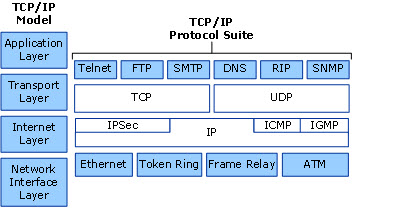
It is a part of the application layer of the TCP/IP reference model.
DNS is widely used in the Internet as well Intranet environments for naming conversions. WINS (Windows internet Naming Service) is the older version of DNS server, which is used to convert the NetBIOS name into an IP address and Vice-Versa.
Namespace, DNS has a hierarchical structure. This means the DNS uses main root or parent domain and sub-root name or child domain. DOT represents the root name.
Domain name is used to create unique names in internet or intranet environments, which are called FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name).
For Example, www.abc.com is a FQDN.
Understanding DNS Zones
DNS typically uses two types of Zones:
Zone is a database structure which contains lists of names and IP addresses. This database structure helps in name conversion (name to IP address mapping) in DNS.
- Forward Lookup Zone: This zone translates alpha-numeric names into IP addresses. This process is called Host record or A-record.
- Reverse Lookup Zone: This zone translates IP addresses into alpha-numeric names. This process is called Pointer record or PTR-record.
Types of DNS Servers
- Primary DNS server: This server has full authority to create and modify the zone. It is also called the Master DNS Server.
- Secondary DNS server: This server is the copy of primary DNS server. No change can be done in this zone. The Secondary DNS server is used as fault-tolerant and load balancing of Primary DNS server.
Active Directory-Integrated DNS server: This DNS server is generally created during the installation of Active Directory. It provides active directory services to the clients.
Caching only DNS server: This DNS server does not contain any zone. It simply stores DNS queries made by the clients. When main DNS servers are not available, client usually refer the query to the Caching only DNS server.